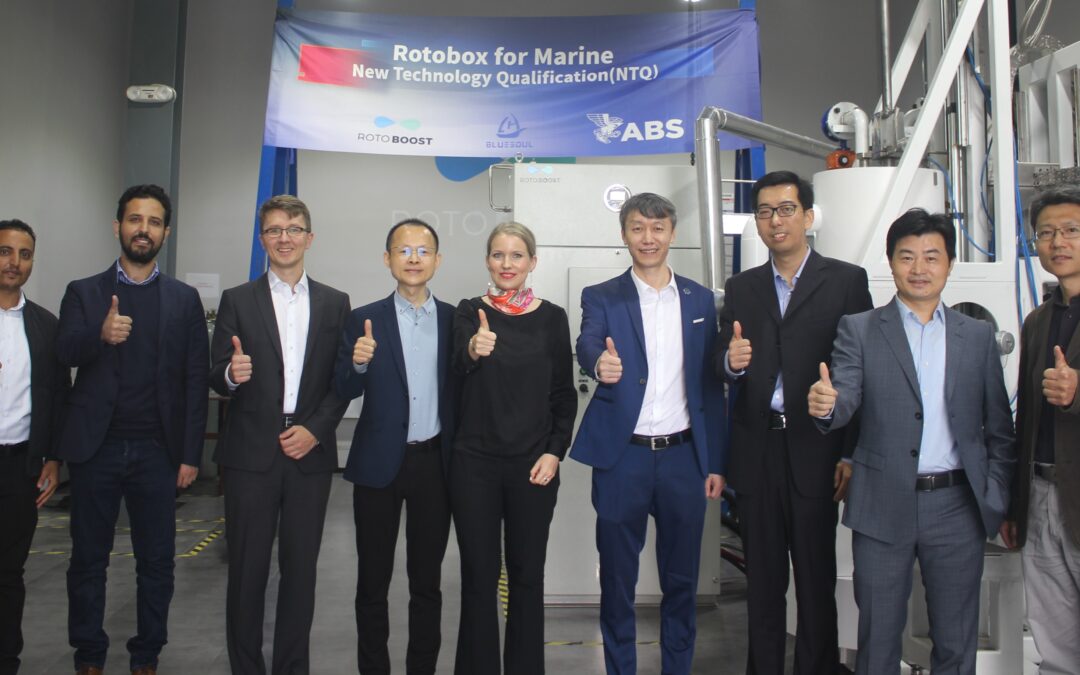
ABS has issued New Technology Qualification for a first-of-its-kind, pre-combustion carbon capture system based on the thermocatalytic decomposition process for ships. Rotoboost, a global hydrogen company based in Norway, developed the system.
Rotoboost’s thermocatalytic decomposition process allows for continuous hydrogen production and carbon capture on board marine vessels. The system converts natural gas into hydrogen and solid carbon with a liquid catalyst.
The resulting gas can be used for fuel cells or as a blend-in fuel for combustion engines or gas-fired boilers. The process can reduce overall carbon emissions by up to 100 per cent depending on the heating method.
Also read: GCMD, OGCI and Stena Bulk kick off shipboard carbon capture project
Reducing methane slip
Using hydrogen as a blend-in fuel promises to significantly reduce the methane slip from combustion engines and reduce particulate matter emissions by capturing carbon in solid form before combustion.
Also read: Approval in principle for Methane Oxidation Catalyst System which targets methane slip
‘Decomposing methane into hydrogen and solid carbon is an intelligent way to implement a carbon capture and storage (CCS) solution on board gas-fuelled ships,’ says Georgios Plevrakis, ABS Vice President, Global Sustainability. ‘This method reduces the storage need on board, and the solid carbon can be used in the production of fuel cells and batteries and can be recycled again and again. This technology is one that promises to accelerate the energy transition, supporting global decarbonisation goals.’
‘The system can be scaled up modularly step-by-step to meet progressing emission regulations while being cost effective for shipowners compared to green fuels or conventional carbon capture systems,’ adds Kaisa Nikulainen, Rotoboost CEO.
Picture by ABS.
Also read: ABS: Green corridors highlight how shipping will drive the energy transition