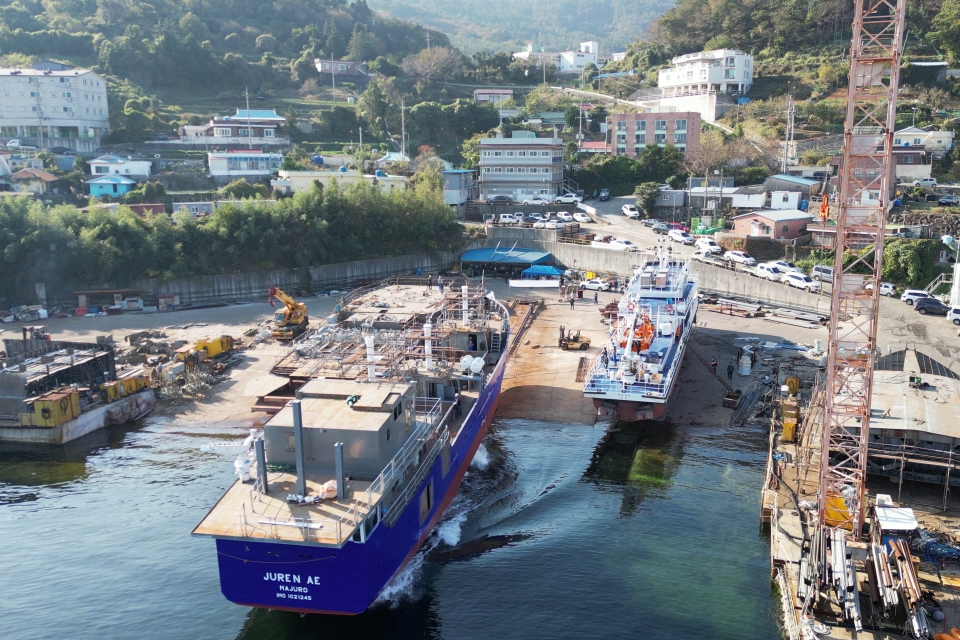
As part of an international climate protection project with the participation of Emden/Leer University of Applied Sciences, the German Society for International Cooperation (GIZ) has commissioned the construction of a new island supply vessel with sail propulsion for largely climate-neutral operation. The ship is being built in Korea and was launched on 15 November.
GIZ is implementing the bilateral project financed by the International Climate Initiative (IKI) together with the government of the Marshall Islands. The ship was developed by the ship design office Kostec Co. and the shipyard Asia Shipbuilding Co. Ltd. in Busan/Geoje, South Korea, together with the Emden/Leer University of Applied Sciences and the Hamburg design office SDC.
After the launch on 15 November, the vessel was moved to the shipyard’s outfitting quay. Briese Research from Leer is also involved in the project to support the construction supervision and commissioning of the ship.
‘We are pleased that the newbuilding has reached this milestone and is now entering the final phase of outfitting,’ says Prof. Captain Michael Vahs from Emden/Leer University of Applied Sciences. ‘This will be very exciting for our construction supervisors in South Korea, as many technical systems now have to be installed and test run. Some fine-tuning is still required. Despite the relatively simple and cost-effective construction concept, there are many innovations in the ship that are exemplary for future zero-emission shipping.’
Also read: TU Delft launches Wind Assisted Ship Propulsion Research Programme
Indosail wind propulsion system
The approximately 48-metre-long, 300-tdw (tons deadweight) island supply vessel for the Marshall Islands is equipped with a semi-automated Indosail wind propulsion system. The sail system, originally developed in Hamburg by naval architect Peter Schenzle (HSVA) for Indonesia, has been adapted to local requirements and is intended to give the ship a speed of up to approximately 12 knots with a sail area of a good 500 m2.
In case of excess sail power, the propeller recuperates and supplies the ship’s electrical system via a hybrid gearbox with attached generator. A powerful battery pack serves as storage. The same generator can act as an electric drive motor on the propeller and be available to the ship for slow manoeuvring.
A diesel engine with a power of approximately 250 kW is installed as a redundancy drive, which guarantees the ship can achieve the required minimum speed of 7 knots even without sail propulsion and under rough sea conditions. In the future, it should also be possible to run the engine on regionally produced biodiesel.
Eighty per cent emissions reduction
Other technical highlights include a high-performance photovoltaic (PV) system for the onboard power supply, as well as new wing keels developed at the Maritime Technical Centre of Emden/Leer University of Applied Sciences, which are intended to give the ship better sailing efficiency and high course stability.
According to model calculations, emissions will be reduced by about eighty per cent, and the goal is to achieve climate neutrality in the long term.
Also read: The winds of change: One zero-emission dilemma for shipping solved?
Further newbuildings
The design office Kostec and the shipyard Asia Shipbuilding want to use the project to create a new foothold for sailing technology and low-emission shipping in the strong Korean shipbuilding market. The cooperation with the Emden/Leer University of Applied Sciences is to be continued for the development of further newbuildings.
This new ship type is to be available in various sizes with different structural and equipment variants according to the customer’s requirements. This also includes a variant with fully automated Flettner rotors.
Training and cooperation
The training concept for the Marshall Islands Shipping Corporation will be developed together with the Emden/Leer University of Applied Sciences, which will support the shipping company in the long term and scientifically evaluate the results of the project. The ability to cooperate with maritime industry partners across the board, from the initial needs analysis through construction to testing and support during the initial operating phase of a ship, is one of the special features of the Fraunhofer Working Group for Sustainable Maritime Mobility (NMM) at Emden/Leer University of Applied Sciences.
The new ship for the Marshall Islands can be inspected by interested shipping companies and shippers after completion, expected in February 2024, during a joint “Open Ship Event” of the partners involved in Geoje, South Korea.
Picture: Launching of the island supply vessel with sail propulsion for the Marshall Islands (by Hochschule Emden/Leer).
Also read: Neptune’s Canopée bags 2023 Ship of the Year Award