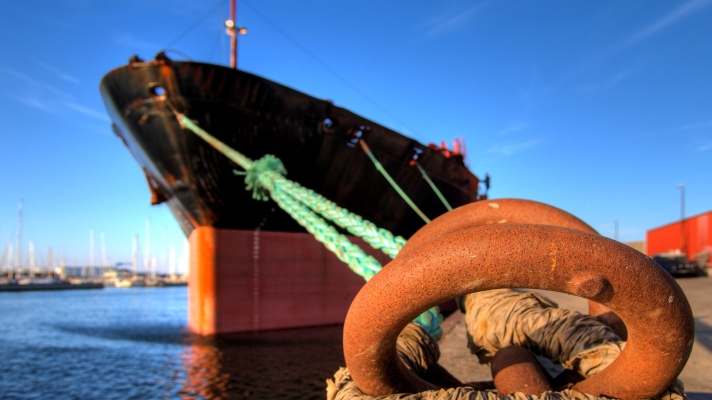
Setting predetermined weather limits to stop cargo ops and/or vacate the berth is a sensible risk reduction measure, according to The Nautical Institute. In a recent Mars Report, a tanker did not adhere to these limits causing the vessel to become adrift.
The Nautical Institute gathers reports of maritime accidents and near-misses. It then publishes these so-called Mars Reports (anonymously) to prevent other accidents from happening. A summary of this incident:
A tanker was berthed port side to, with all lines run ashore except for the headlines, which were secured to a mooring buoy. Cargo discharge operations were begun, but the weather conditions were not very favourable: the wind was blowing 22-27 knots, with some stronger gusts. The cargo operation was not stopped or suspended even though the countersigned ship/shore checklist indicated the following operational weather limitations:
- Wind 25 knots: Stop cargo operation.
- Wind 35 knots: Disconnect cargo arms.
- Wind 40 knots: Vessel to vacate berth.
By 01.18 discharging was completed and shore staff disconnected the cargo hose within fifteen minutes. Wind strength had increased further and local pilots had rescheduled departure.
At 02.36, a strong gust of 65+ knots caused the forward mooring buoy chain to fail. The bow started to swing sharply to starboard, pushed by the wind, and in short order other lines began to fail. Soon, the vessel was connected only by the aft stern lines. The master quickly activated the general alarm. Ten minutes later, the main engine was ready, but pilots and tugs were not available. The stern lines were cut and the vessel was clear of the berth. The vessel was successfully turned on to a course of about 275 degrees while the master was in radio contact with pilots. Due to the strong wind, and hindered by the mooring buoy still connected to the vessel’s forward lines, the vessel lost steerage, running aground in shallow water while still in the port.
Investigation findings
The company investigation found, among others, that:
- The mooring buoy was not suitable to accommodate the four mooring lines forward. There was no indicated safe working load (SWL).
- The Navtex was not set to the local radio station, therefore local warnings were not received.
- The master and officer of the watch had not developed or discussed any specific emergency plan to vacate the berth.
Also read: Vessel goes adrift and hits pier after bollard fails
Advice from The Nautical Institute
- Setting predetermined weather limits to stop cargo ops and/or vacate the berth is a sensible risk reduction measure. Be sure to follow them.
- Close and continued attention to local weather conditions and warnings, at sea or while at berth, is one of the mariner’s most important duties.
- Commercial pressures are sometimes at cross-purposes with vessel safety; which one do you favour?
Mars Reports
This accident was covered in the Mars Reports, originally published as Mars 202134, that are part of Report Number 345. A selection of this Report will also be published in SWZ|Maritime’s September 2021 issue. The Nautical Institute compiles these reports to help prevent maritime accidents. That is why they are also published on SWZ|Maritime’s website.
More reports are needed to keep the scheme interesting and informative. All reports are read only by the Mars coordinator and are treated in the strictest confidence. To submit a report, please use the Mars report form.